Understanding Blood Glucose
Role of Blood Glucose in the Body
- Glucose serves as the primary source of energy for cells throughout the body, fueling essential functions such as metabolism, movement, and cognitive processes.
- After consuming carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks them down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream to be transported to cells via insulin.
- Proper regulation of blood glucose levels is critical for maintaining energy balance and supporting overall health and well-being.
Factors Affecting Blood Glucose Levels
- Diet: The type and quantity of carbohydrates consumed directly impact blood glucose levels. Foods with a high glycemic index cause rapid spikes, while fiber-rich foods and complex carbohydrates lead to slower, steadier increases.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to better absorb glucose from the bloodstream, thereby lowering blood sugar levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents, can affect blood glucose levels by either lowering them (hypoglycemic agents) or raising them (e.g., corticosteroids).
- Stress: Stress hormones like cortisol can trigger the release of glucose into the bloodstream, leading to temporary spikes in blood sugar levels.
Common Conditions Related to Blood Glucose Imbalance
- Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to insufficient insulin production or ineffective insulin action. Type 1 diabetes involves autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells, while type 2 diabetes typically results from insulin resistance and impaired beta cell function.
- Hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia occurs when blood glucose levels drop below normal, leading to symptoms such as shakiness, sweating, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. It is commonly associated with diabetes treatment, particularly insulin therapy.
- Hyperglycemia: Hyperglycemia refers to abnormally high blood glucose levels, often observed in individuals with diabetes who fail to adequately manage their condition. Prolonged hyperglycemia can result in complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage.
Understanding these aspects of blood glucose is crucial for promoting metabolic health and preventing the onset of serious medical conditions. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels through testing enables individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise regimen, and medical treatment, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
Types of Blood Glucose Tests
Fasting Blood Glucose Test
- This test measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast, typically lasting 8 to 12 hours.
- It is often used to diagnose diabetes and assess glycemic control in individuals with known diabetes.
- A blood sample is drawn from a vein in the arm and analyzed in a laboratory. Normal fasting blood glucose levels range from 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
- The OGTT involves fasting overnight, followed by the consumption of a glucose-rich beverage containing a standardized amount of glucose (usually 75 grams).
- Blood samples are taken at specific intervals, typically at 1, 2, and sometimes 3 hours after consuming the glucose solution, to assess how the body processes glucose over time.
- This test is used to diagnose gestational diabetes in pregnant women and to evaluate impaired glucose tolerance or insulin resistance in non-pregnant individuals.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Test
- The HbA1c test provides an estimate of average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months by measuring the percentage of hemoglobin that is glycated (i.e., bound to glucose).
- It does not require fasting and can be performed at any time of the day.
- HbA1c levels are expressed as a percentage of total hemoglobin. Normal levels typically fall below 5.7%, while levels of 6.5% or higher indicate diabetes.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
- CGM involves the use of a small sensor inserted under the skin, usually on the abdomen, to measure interstitial glucose levels continuously throughout the day and night.
- The sensor transmits glucose readings wirelessly to a monitoring device or smartphone app, providing real-time data on blood sugar trends and fluctuations.
- CGM is particularly useful for individuals with diabetes who require frequent glucose monitoring to optimize insulin therapy, detect hypo- and hyperglycemia, and make informed decisions about diet and exercise.
These various wellness tests play essential roles in diagnosing diabetes, monitoring glycemic control, and assessing overall metabolic health. Depending on individual needs and clinical indications, healthcare providers may recommend specific tests to evaluate blood sugar levels and guide treatment decisions.
Blood Glucose Testing at Home
Benefits of having Blood Glucose Testing at Home:
- Convenience: One of the primary benefits of blood glucose testing at home is the convenience it offers. Individuals can perform the test in the comfort of their own homes without the need to visit a healthcare facility.
- Ease of Use: Modern blood glucose testing kits are designed to be user-friendly, allowing individuals to perform the test with minimal hassle. Clear instructions and simple procedures make it easy for anyone to monitor their blood glucose levels at home.
- Time-saving: Home blood glucose testing eliminates the need for travel to a medical facility and waiting for appointments, saving valuable time for individuals with busy schedules.
- Privacy: Testing at home provides privacy and discretion, allowing individuals to monitor their blood glucose levels discreetly without the need for public exposure.
- Regular Monitoring: For individuals with diabetes or at risk of diabetes, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential for effective management. Testing at home enables frequent monitoring, allowing for better control of blood sugar levels.
- Empowerment: Home testing empowers individuals to take control of their health and become more actively involved in managing their condition. By regularly monitoring their blood glucose levels, individuals can make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication adjustments.
- Early Detection: Regular home testing facilitates early detection of any fluctuations or abnormalities in blood glucose levels, enabling prompt intervention and prevention of complications associated with diabetes.
- Peace of Mind: For individuals living with diabetes, regular home blood glucose testing provides peace of mind knowing that they are actively monitoring their condition and taking proactive steps to maintain optimal health.
- Cost-effective: In the long run, home blood glucose testing can be cost-effective compared to frequent visits to healthcare facilities for testing. It eliminates transportation costs and reduces the need for professional assistance for routine monitoring.
- Integration with Telemedicine: With advancements in technology, home blood glucose testing can be seamlessly integrated with telemedicine platforms, allowing individuals to share their results with healthcare providers for remote monitoring and management.
Indications for Blood Glucose Testing
Symptoms Indicating Potential Blood Glucose Issues
- Frequent Urination: Increased urination, especially during the night, can be a sign of elevated blood glucose levels.
- Excessive Thirst: Persistent thirst, even after drinking plenty of fluids, may indicate dehydration due to high blood sugar.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden or unexplained weight loss can occur in individuals with poorly controlled diabetes due to the body’s inability to utilize glucose effectively.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Persistent fatigue and weakness may result from inadequate glucose delivery to cells for energy production.
- Blurred Vision: Fluctuations in blood glucose levels can affect the shape of the eye lens, leading to blurry vision.
- Slow Wound Healing: High blood sugar levels can impair circulation and immune function, delaying the healing of cuts, bruises, and infections.
- Frequent Infections: Individuals with poorly controlled diabetes are more susceptible to infections, such as urinary tract infections, skin infections, and yeast infections.
Screening for Diabetes Risk Factors
- Overweight or Obesity: Excess body weight, especially abdominal fat, increases the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Family History: Having a close relative with diabetes, particularly a parent or sibling, raises the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary lifestyle and lack of regular exercise contribute to insulin resistance and diabetes risk.
- Age Over 45: Risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after 45 years old.
- Gestational Diabetes: Women who had gestational diabetes during pregnancy or gave birth to a baby weighing over 9 pounds are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS have an increased risk of insulin resistance and diabetes due to hormonal imbalances.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels in Diabetes Management
- Type 1 Diabetes: Individuals with type 1 diabetes require regular blood glucose testing to adjust insulin doses, prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), and maintain optimal glycemic control.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Blood glucose monitoring is essential for individuals with type 2 diabetes to assess the effectiveness of lifestyle modifications, oral medications, or insulin therapy in managing blood sugar levels.
- Gestational Diabetes: Pregnant women diagnosed with gestational diabetes need frequent blood glucose testing to ensure adequate glycemic control and reduce the risk of complications for both mother and baby.
- Pre-Diabetes: People with pre-diabetes undergo blood glucose testing to monitor their progression to type 2 diabetes and implement preventive measures such as diet, exercise, and weight management.
Regular blood glucose testing plays a crucial role in identifying individuals at risk for diabetes, diagnosing the condition in its early stages, and optimizing diabetes management to prevent complications and promote overall health and well-being.
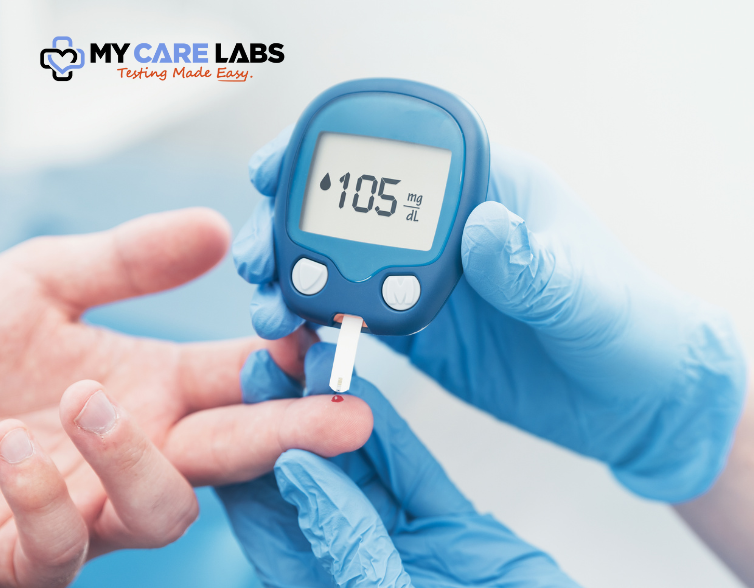
Blood Glucose Testing Machines
Blood glucose testing machines, also known as glucometers, are essential tools for individuals managing diabetes or monitoring blood sugar levels for health purposes. These devices allow users to measure their blood glucose levels quickly and accurately at home or on the go. Here are some key points about blood glucose testing machines:
- Accuracy: Blood glucose testing machines are designed to provide accurate measurements of blood sugar levels, helping individuals make informed decisions about their health and diabetes management.
- Portability: Most blood glucose testing machines are compact and lightweight, making them easy to carry around for testing whenever and wherever needed.
- Ease of Use: These machines typically come with user-friendly features such as large display screens, simple navigation buttons, and step-by-step instructions, making them easy for individuals of all ages to use.
- Fast Results: Blood glucose testing machines deliver fast results, allowing users to obtain their blood sugar readings within seconds, enabling prompt action if necessary.
- Memory Storage: Many modern blood glucose testing machines have built-in memory storage, allowing users to track their blood sugar levels over time and share the data with healthcare providers for better management.
- Variety of Options: There are various blood glucose testing machines available in the market, offering different features, price points, and testing methods to suit individual preferences and needs.
Blood glucose testing machines play a crucial role in diabetes management and monitoring blood sugar levels, empowering individuals to take control of their health and well-being.
Procedure and Preparation for Blood Glucose Testing
Pre-test Instructions and Dietary Restrictions
- Fasting: Some blood glucose tests, such as fasting blood glucose and oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT), require fasting for a certain period, typically 8 to 12 hours, before the test. During fasting, you should abstain from eating or drinking anything other than water.
- Medication Adjustments: Inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking, as certain drugs can affect blood glucose levels. Your doctor may recommend adjusting or temporarily discontinuing medications before the test.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: Refrain from consuming alcoholic beverages and caffeinated products, as they can interfere with blood glucose measurements.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water before fasting to prevent dehydration and facilitate blood sample collection.
Steps Involved in Different Blood Glucose Tests
Fasting Blood Glucose Test:
- Schedule the test in the morning after an overnight fast.
- Visit the laboratory or healthcare facility where a healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from a vein in your arm using a needle.
- The collected blood sample is then analyzed to measure fasting blood glucose levels.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT):
- Begin fasting overnight before the test.
- On the morning of the test, visit the laboratory or healthcare facility.
- A baseline blood sample is collected to measure fasting blood glucose levels.
- You will be asked to drink a glucose solution containing a specific amount of glucose.
- Blood samples are collected at specified intervals, usually every 30 to 60 minutes, over a period of two hours to monitor how your body metabolizes glucose.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Test:
- No special preparation, such as fasting, is required for this test.
- A blood sample is collected from a vein in your arm by a healthcare professional.
- The collected blood sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis to determine the average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM):
- CGM involves wearing a small sensor, usually on the abdomen or arm, that continuously measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid.
- The sensor is connected to a transmitter that wirelessly sends glucose readings to a receiver or smartphone device.
- Users can track their glucose levels in real-time and receive alerts for high or low blood sugar levels.
Tips for Accurate Testing and Interpretation of Results
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Adhere to any pre-test instructions provided by your healthcare provider to ensure accurate results.
- Stay Calm and Relaxed: Stress and anxiety can affect blood glucose levels. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing before and during the test.
- Keep Records: Maintain a log of your blood glucose test results, including date, time, and corresponding values, to track changes over time and discuss with your healthcare provider.
- Discuss Results with Your Doctor: After obtaining the test results, schedule a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider to review the findings, discuss implications, and develop a personalized plan for managing your blood glucose levels.
By following these steps and guidelines, you can prepare effectively for blood glucose testing, ensure accurate results, and facilitate the interpretation of test findings for optimal health management.
Interpreting Blood Glucose Test Results
Normal Ranges for Blood Glucose Levels
- Fasting Blood Glucose: Typically, normal fasting blood glucose levels range between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or 3.9 to 5.6 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Values within this range indicate healthy blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Normal blood glucose levels two hours after consuming a glucose solution during an OGTT usually fall below 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L).
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c): The normal range for HbA1c levels is typically below 5.7%, indicating good long-term blood glucose control. However, the target range may vary based on individual health status and treatment goals.
Abnormal Findings and Their Significance
- Hyperglycemia: Elevated blood glucose levels, known as hyperglycemia, may indicate prediabetes or diabetes mellitus. Fasting blood glucose levels above 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or HbA1c levels exceeding 6.5% on two separate occasions suggest diabetes diagnosis.
- Hypoglycemia: Low blood glucose levels, termed hypoglycemia, can result from excessive insulin or diabetes medication, delaying or skipping meals, or strenuous physical activity. Symptoms of hypoglycemia may include dizziness, confusion, sweating, and palpitations.
- Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT): Intermediate blood glucose levels observed during an OGTT, typically between 140 and 199 mg/dL (7.8 to 11.0 mmol/L), indicate impaired glucose tolerance, a precursor to diabetes.
Follow-up Testing and Consultations Based on Results
- Confirmatory Testing: If initial blood glucose tests reveal abnormal findings suggestive of diabetes or prediabetes, healthcare providers may recommend additional confirmatory tests to validate the diagnosis. These tests may include repeat fasting blood glucose tests, OGTTs, or HbA1c measurements.
- Diagnostic Evaluation: Following abnormal blood glucose results, individuals may undergo a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation to assess overall health status, identify underlying causes of glucose abnormalities, and evaluate for potential complications associated with diabetes.
- Treatment Planning and Monitoring: Based on diagnostic findings, healthcare professionals develop personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs, incorporating lifestyle modifications, medication management, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. Patients receive education and support to effectively manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
- Long-term Management: Continuous monitoring and periodic reassessment of blood glucose levels are essential components of long-term diabetes management. Regular follow-up consultations with healthcare providers facilitate ongoing evaluation, adjustment of treatment regimens, and implementation of preventive measures to optimize health outcomes and enhance quality of life.
Understanding and interpreting blood glucose test results empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health, facilitating timely intervention, and promoting overall well-being. By collaborating with healthcare professionals and adhering to recommended guidelines, individuals can effectively navigate the complexities of blood glucose monitoring and achieve optimal health outcomes.
Blood Glucose Test a1c
The blood glucose test A1c, also known as the hemoglobin A1c test, is a crucial tool in managing diabetes and assessing long-term blood sugar control. Here are some key points about the blood glucose test A1c:
- Measuring Blood Sugar Levels: The blood glucose test A1c measures the average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months by assessing the percentage of hemoglobin that has glucose attached to it.
- Long-term Control: Unlike other blood glucose tests that provide a snapshot of blood sugar levels at a specific moment, the A1c test reflects average blood sugar levels over a more extended period, offering insight into long-term diabetes management.
- Diabetes Management: Healthcare providers use the A1c test to monitor blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes, helping to adjust treatment plans, medications, and lifestyle interventions as needed to achieve optimal blood sugar levels.
- Risk Assessment: The A1c test also serves as a valuable tool for assessing the risk of diabetes complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage, as higher A1c levels are associated with an increased risk of these complications.
- Regular Monitoring: Individuals with diabetes typically undergo A1c testing every three to six months, depending on their treatment plan and overall health status, to track their blood sugar control and make necessary adjustments to their diabetes management regimen.
The blood glucose test A1c plays a vital role in diabetes management by providing valuable information about long-term blood sugar control and helping individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their health and treatment.
Importance of Early Detection and Management
Benefits of Early Detection of Blood Glucose Abnormalities
- Timely Intervention: Early detection of blood glucose abnormalities, such as prediabetes or diabetes, allows for prompt intervention and management, minimizing the risk of progression to more severe health complications.
- Preventive Measures: Identifying high-risk individuals through screening programs enables early implementation of preventive measures to mitigate the development of diabetes and its associated complications.
- Improved Health Outcomes: Early detection facilitates timely initiation of treatment interventions, leading to improved glycemic control, reduced disease burden, and enhanced overall health outcomes.
- Cost Savings: Detecting blood glucose abnormalities in the early stages can result in cost savings by averting the need for more intensive and expensive medical interventions to manage advanced disease states.
Lifestyle Modifications for Blood Glucose Management
- Healthy Eating Habits: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports blood glucose management and helps prevent fluctuations in sugar levels.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood glucose levels, and maintain a healthy weight.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight through a combination of healthy eating and regular exercise reduces the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Stress Reduction: Implementing stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices, helps lower cortisol levels and promotes better blood glucose control.
Strategies for Preventing Diabetes Complications
- Regular Monitoring: Routine monitoring of blood glucose levels, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and kidney function allows for early detection of complications and timely intervention to prevent their progression.
- Medication Adherence: Strict adherence to prescribed medications, including oral antidiabetic drugs or insulin therapy, helps maintain optimal blood glucose levels and reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Foot Care: Proper foot care practices, such as daily inspection, wearing comfortable footwear, and moisturizing dry skin, prevent diabetic foot ulcers and reduce the risk of lower limb amputations.
- Eye and Dental Examinations: Regular eye exams and dental check-ups help identify and address diabetes-related eye diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy, and oral health issues, including gum disease and tooth decay, at an early stage.
Early detection and proactive management of blood glucose abnormalities are critical for preserving health and preventing the onset and progression of diabetes and its associated complications.
By embracing healthy lifestyle habits, adhering to medical recommendations, and prioritizing preventive care, individuals can optimize their blood glucose control and enjoy a higher quality of life.